
How to Calculate Age in Excel Using Formula?
Calculating age is one of the most common tasks encountered in Excel – employee records, student lists, customer reports, and so on. Many users will try to subtract dates in a manual way or confuse themselves with complicated logic, but Excel provides us easy and accurate ways to calculate age in years, months and even days.
In this blog, we will show you the quickest and easiest way to calculate age in Excel.
Why Do You Need an Age Formula?
- Age calculation comes up in various scenarios:
- HR teams managing employee DOB and retirement planning
- Schools and universities maintaining student details
- Healthcare or insurance companies checking eligibility
- Customer segmentation in marketing campaigns
- Instead of doing it manually, Excel makes the process automatic and error-free.
The Simplest Formula: Using DATEDIF()
The hidden gem in Excel for age calculation is the DATEDIF() function.
Formula:
=DATEDIF(B2, TODAY(), “Y”)
Here’s how it works:
B2 → Cell containing Date of Birth (DOB)
TODAY() → Returns the current date
“Y” → Calculates the difference in completed years
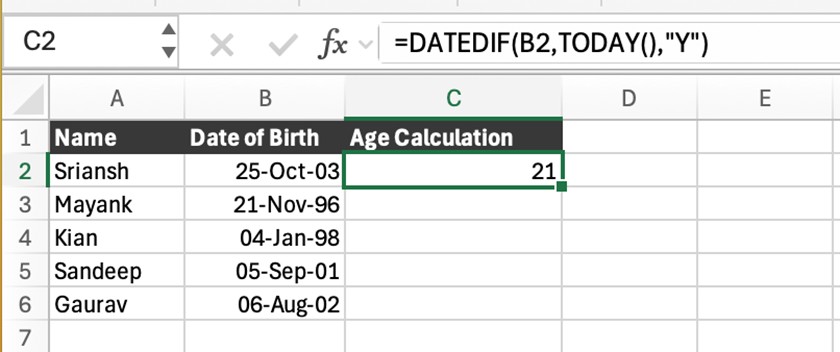
Example:
If B2 = 25-Oct-2003, the formula will return 21 (as of 25-Sep-2025).
Extend the Formula: Years, Months & Days
You can go a step further and calculate a detailed age:
=DATEDIF(B2, TODAY(), “Y”) & ” Years, ” & DATEDIF(B2, TODAY(), “YM”) & ” Months, ” & DATEDIF(B2, TODAY(), “MD”) & ” Days”
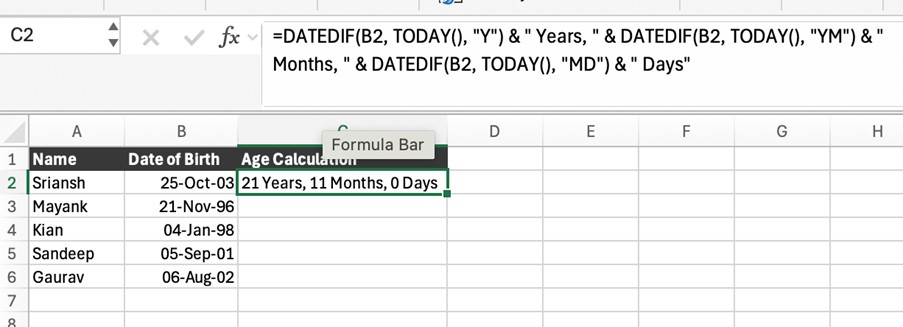
This returns something like:
21 Years, 11 Months, 0 Days
Perfect if you need an exact age breakdown.
Quick Alternatives
Simple Year Difference (not always accurate):
=YEAR(TODAY()) – YEAR(B2)
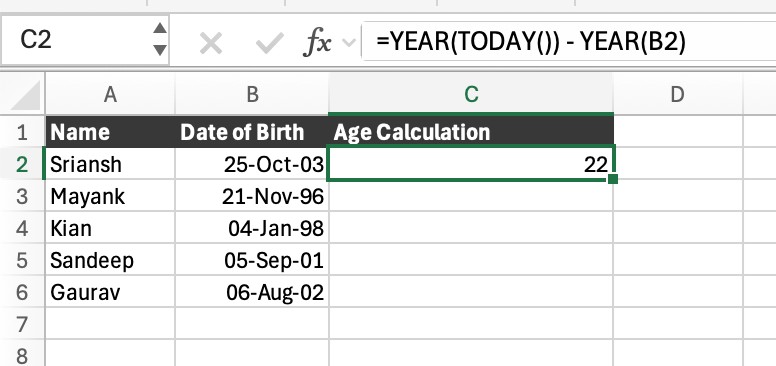
But this can overstate the age if the birthday hasn’t occurred yet this year.
Pro Tip
Always make sure your DOB column is formatted as a valid date.
If you get errors with DATEDIF(), recheck the date format.
Conclusion
The fastest and simplest way to calculate age in Excel is with the DATEDIF() function. With just one formula, you can calculate age in years or even get a detailed breakdown of years, months, and days.
Note:- DATEDIF function is the hidden function in Excel, type the complete name of function and start entering the reference.
So, the next time you’re working with DOB data, let Excel do the hard work for you!




